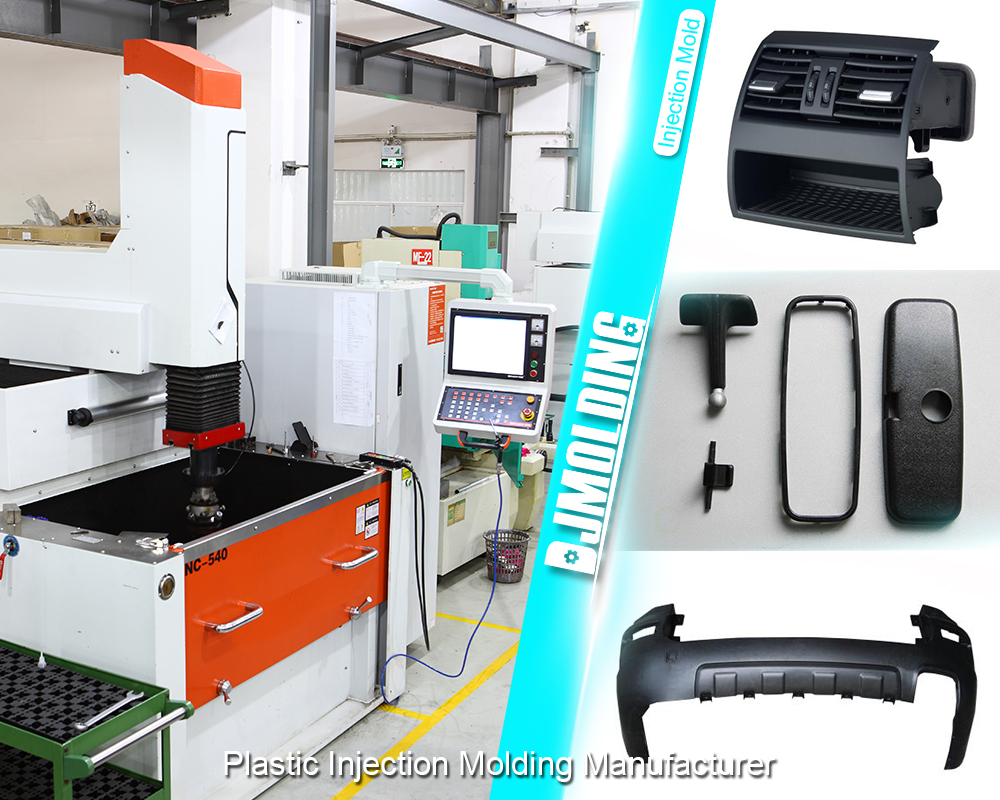
Injection Molding vs. Thermoforming: A Comprehensive Comparison
Injection Molding vs. Thermoforming: A Comprehensive Comparison
In the manufacturing industry, the choice of production method is crucial to the final product’s efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Injection molding and thermoforming are two widely used plastic forming techniques, each with advantages and applications. This article compares injection molding and thermoforming, exploring their processes, materials, advantages, disadvantages, applications, and future trends.
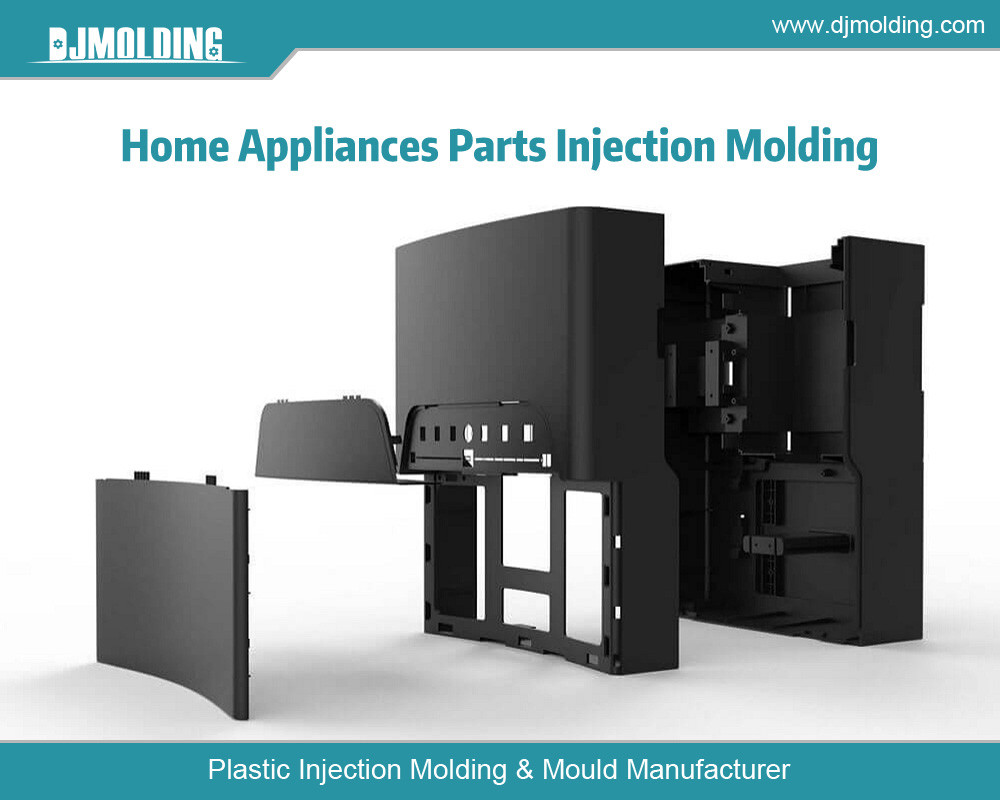
Overview of Injection Molding
The Injection Molding Process
Injection molding involves the creation of parts by injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity. The process begins with melting plastic pellets, which are then injected into a high-precision mold under pressure. The mold is opened once the plastic cools and solidifies, and the finished part is ejected. The cycle then repeats for the next part.
Materials Used in Injection Molding
Injection molding can utilize a wide range of thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Common materials include:
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
Each material offers different properties, making it suitable for specific applications.
Advantages of Injection Molding
- High Precision and Repeatability: Injection molding produces highly accurate parts with consistent quality.
- Efficiency in Mass Production: Once the mold is created, parts can be produced rapidly, making it ideal for large-scale production.
- Material Versatility: A wide range of materials can be used, allowing for the creation of parts with diverse properties.
- Complex Geometry: Injection molding can produce parts with intricate designs and fine details.
Disadvantages of Injection Molding
- High Initial Costs: The creation of molds is expensive and time-consuming.
- Long Lead Times: The development of molds can extend the time to market for new products.
- Limited Material Selection for Certain Applications: Some materials may not be suitable for injection molding due to their properties.
Applications of Injection Molding
Injection molding is used in various industries, including:
- Automotive: Manufacturing of dashboards, bumpers, and interior components.
- Consumer Goods: Production of household items, toys, and electronics.
- Medical: Creation of syringes, medical devices, and laboratory equipment.
- Packaging: Production of bottle caps, containers, and lids.
Overview of Thermoforming
The Thermoforming Process
Thermoforming involves heating a plastic sheet until it becomes pliable, then forming it over a mold using vacuum, pressure, or mechanical force. Once the plastic cools, it retains the shape of the mold. There are two main types of thermoforming: vacuum forming and pressure forming.
Materials Used in Thermoforming
Thermoforming typically uses thermoplastic sheets. Common materials include:
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
- High-impact polystyrene (HIPS)
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Advantages of Thermoforming
- Lower Initial Costs: The molds used in thermoforming are generally less expensive than those for injection molding.
- Shorter Lead Times: Molds are quicker to produce, allowing for faster time to market.
- Large Part Production: Thermoforming is suitable for creating large parts, such as automotive panels and signage.
- Flexibility in Material Thickness: Thermoforming can handle a variety of sheet thicknesses, making it versatile for different applications.
Disadvantages of Thermoforming
- Less Precision: Compared to injection molding, thermoforming offers lower precision and detail.
- Limited Complexity: It is less suitable for parts with intricate geometries and fine details.
- Higher Material Waste: The process can generate more scrap material, significantly when cutting out parts from the formed sheet.
Applications of Thermoforming
Thermoforming is widely used in:
- Packaging: Blister packs, clamshells, and trays.
- Automotive: Interior panels, dashboards, and components.
- Consumer Products: Plastic cups, containers, and housings.
- Medical: Disposable trays and packaging for medical devices.
Injection Molding vs. Thermoforming: A Detailed Comparison
Cost Considerations
Initial Investment
- Injection Molding: Requires significant investment in mold creation, which is cost-prohibitive for low-volume production.
- Thermoforming: Involves lower mold costs, making it more economical for smaller production runs and prototyping.
Production Costs
- Injection Molding: Offers lower per-unit costs for high-volume production due to the efficiency of the process.
- Thermoforming: This may have higher per-unit costs for large volumes but is cost-effective for lower quantities.
Production Speed
- Injection Molding: Once the mold is ready, the cycle time for each part is very short, allowing for rapid production.
- Thermoforming: Generally faster to set up and start production but slower in cycle time for each part than injection molding.
Material Efficiency
- Injection Molding: Produces less waste as the material is injected directly into the mold cavity.
- Thermoforming: Often results in more waste due to the trimming and cutting of formed sheets.
Part Design and Complexity
- Injection Molding: Ideal for complex parts with detailed geometries and tight tolerances.
- Thermoforming: Better suited for more straightforward, more significant parts with less intricate details.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics
- Injection Molding: Capable of producing high-quality surface finishes and detailed textures.
- Thermoforming: Surface finish quality can vary, requiring additional finishing steps for high-quality aesthetics.
Environmental Impact
- Injection Molding: Generally more efficient with material usage, but the high energy consumption for mold creation and the process can be a concern.
- Thermoforming: Produces more scrap material, which can be recycled, but the process is typically less energy-intensive.
Future Trends and Innovations
Sustainable Materials and Processes
Both injection molding and thermoforming are seeing advancements in using sustainable materials, such as biodegradable plastics and recycled polymers. Process efficiency and waste reduction innovations are also driving the industry towards more environmentally friendly practices.
Technological Advancements
- Automation: Increased use of automation and robotics enhances precision, reduces labor costs, and improves production speed in both processes.
- 3D Printing: Integrating 3D printing for mold creation and prototyping reduces lead times and costs for injection molding and thermoforming.
- Smart Manufacturing: The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is optimizing production processes, improving quality control, and reducing downtime.
Market Trends
- Customization and Flexibility: The demand for customized products pushes manufacturers to adopt more flexible and adaptable production methods.
- Medical and Healthcare: Growth in the medical and healthcare sectors drives innovation in material properties and production techniques to meet stringent regulatory requirements.
- Consumer Electronics: The increasing complexity and miniaturization of electronic devices create new challenges and opportunities for injection molding and thermoforming.
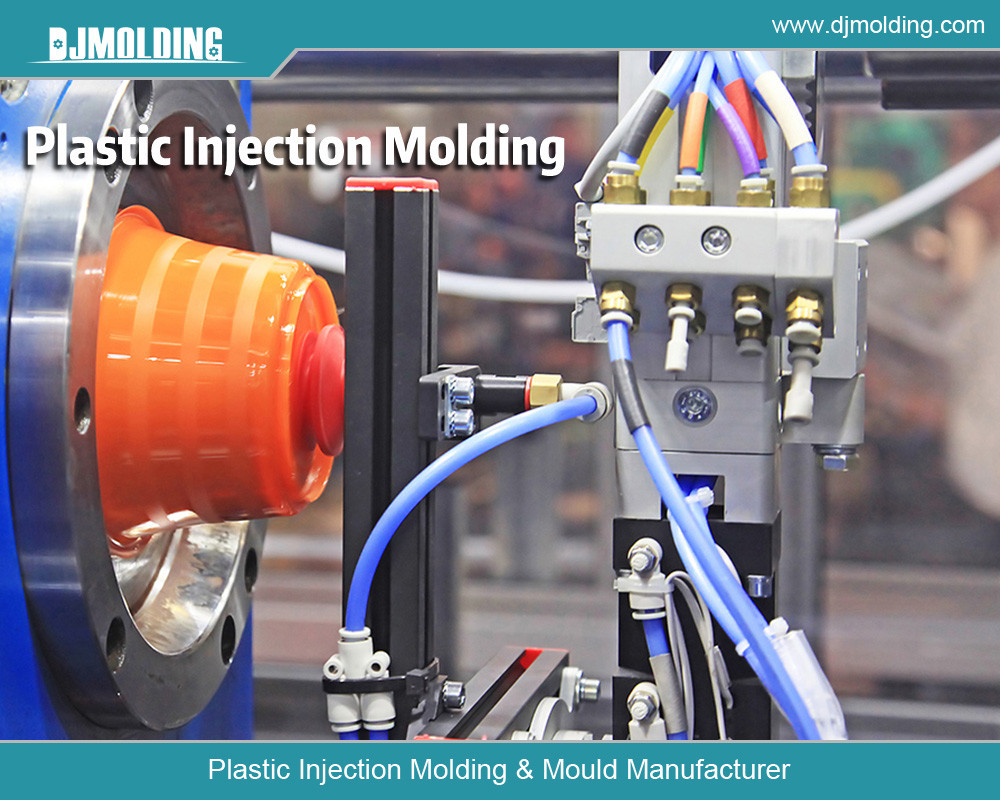
Conclusion
Injection molding and thermoforming are two essential plastic forming techniques, each with strengths and limitations. The choice between the two depends on factors such as production volume, part complexity, cost considerations, and material requirements. By understanding each process’s key differences and advantages, manufacturers can make informed decisions to optimize their production strategies and meet the demands of their specific applications.
Staying abreast of technological advancements and market trends in a rapidly evolving industry is crucial for maintaining competitiveness. As injection molding and thermoforming continue to innovate and adapt, they will remain vital components of modern manufacturing, offering versatile solutions for various products and industries.
For more about the injection molding vs. thermoforming: a comprehensive comparison,you can pay a visit to Djmolding at https://www.djmolding.com/thermoplastic-injection-molding/ for more info.




