Rapid Prototyping Service

Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is the process of developing prototypes for products as fast as possible. Prototyping is an integral part of product development. It’s where design teams create an experimental product to apply their ideas.
Rapid Prototyping Definition
It is the process of developing prototypes as fast as possible to emulate a final product design. It is a series of techniques used to model a scale prototype of a physical component or an assembly using CAD data.
Designers usually complete the process using additive manufacturing or 3D printing. Compared to traditional subtractive methods, additive manufacturing does not need tooling. It offers you an almost unlimited type of freedom in fabricating prototypes.
Problem: Functional prototypes often requires similar processes and resources to producing finished products. Traditional production processes like CNC machining or injection molding are expensive and slow. These need tools acquisition and setup; hence making custom prototyping expensive and slow.
Solution: Rapid or fast prototyping aids organizations in transforming ideas into real products. It helps turn concepts into quality prototypes that look like finished products. Engineers and product designers can develop prototypes from computer-aided design (CAD) data faster. They can also apply quick changes on their designs based on the feedback acquired.

Different Types of Rapid Prototyping
Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA was the first successful technique used for commercial 3D printing. It is a rapid prototyping process that is fast and less costly. It uses solidified photosensitive liquid to develop a prototype design, layer by layer. The liquid is often solidified using a computer-generated UV light.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS helps in both plastic and metal prototyping. With the help of a powder bed, it builds a prototype layer-by-layer, using a laser to heat and sediment the powdered substance. However, the prototyped parts are not as strong as those produced by stereolithography. The surface of your final product is often rough and might need some more work to make it presentable.
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM)
FDM is a less expensive and easy-to-use process. It’s found in most non-industrial 3D desktop. A spool of thermoplastic filament is melted and the resulting liquid is layered to create a 3D design. During the early times of use for 3D printing, FDM resulted in weak resolute designs. But, the process is improving, making it ideal for product development.
Binder Jetting
Binder jetting technique enables you to print one or more parts at once. Even so, the parts created are not strong enough compared to those from the SLS. Like SLS though, this process involves the use of a powder bed to layer the prototyped parts.
5 Benefits of Rapid Prototyping
Businesses need to create and introduce new commodities faster for the growing consumermarket. For your company to enjoy massive success, rapid prototyping is necessary. Fasterproduct development and technology innovation are key to a firm’s success. Hence, it is themost important element of new product development, Here are some advantages:
1.Realize new concepts and ideasfaster through a tangible product
2.Innovate concepts and ideas from end-user and team feedback before final product
3.lterate form and fit of thedesigns faster
4.Effective functionality troubleshooting thus reducing risks
5.Decreases product design anddevelopment time & cost
Importance of Rapid Prototyping
Businesses need to create and introduce new commodities faster for the growing consumer market. For your company to enjoy massive success, rapid prototyping is necessary. Faster product development and technology innovation are key to a firm’s success. Hence, it is the most important element of new product development. Here are some advantages:
Realize and Explore New Concepts Faster
Rapid prototyping enables you to apply new concepts and ideas into an experimental model faster. You will also be able to understand the appearance and feel of the prototype design in real life.
Communicate Ideas Effectively
Rapid prototyping allows you to get precise and useful user feedback. This is important to help you understand what the user need and want. You can then restructure and refine your designs effectively. A rapid prototype model helps designers and engineers to visualize their ideas to the relevant people.
Design Iteratively and Instantly Incorporate Changes
Prototyping goes through testing, assessment, and polishing before obtaining a finished product. Rapid prototyping allows for flexibility in creating more realistic prototypes. It also enhances the instant implementation of changes in prototype products.
Applications of Rapid Prototyping
Companies use rapid prototyping to test size and fit of products before moving to mass production.
This technique was used to develop scale models and physical parts for the automobile industry. But, the technique has been adopted across multiple industries like aerospace, and the medical sector.
DJmolding Rapid Prototyping Manufacturing Services
CNC Machining
CNC machining is ideal for making high-quality rapid prototypes from plastic or metal without investing in expensive tooling. Your parts will achieve tighter tolerances with better surface finishes than with other prototyping methods. We can also machine all the features needed for a fully functional part, including tapped and threaded holes and precisely flat surfaces.
We have over 30 CNC mills, lathes and EDM machines in-house for all your CNC needs. We also have a multilingual support team to ensure your product development journey is smooth and worry free. Learn more about our CNC machining service.
Metal 3D Printing
Metal 3D printing is ideal for making complex shapes that combine light weight with high strength. You don’t need to invest in hard tooling and parts can be printed in hours rather than days or weeks.
We use a state-of-the-art Renishaw AM250 printer to create fully dense parts for ultimate performance. Just as importantly, we have expert technicians in-house who provide you with an unparalleled degree of engineering expertise to ensure you get the highest quality finished product. Find out more about our 3D metal printing service.
Vacuum Casting
Polyurethane vacuum casting molds create up to 30 high-fidelity copies from your original master pattern. Parts can be molded in a variety of resins, including engineering grade plastics, and even overmolded in multiple materials.
We are experts in making production quality cast copies from master patterns. Not only will you benefit from our exceptional attention to detail, but we also provide a full suite of finishing services to bring your part up to showroom quality. Learn more about what our vacuum casting service can do for you.
SLA/SLS
SLA and SLS are two of the earliest 3D printing or additive manufacturing processes for plastic. Not only are these techniques fast, but they allow you to produce complex internal features impossible to make with traditional manufacturing. We use SLA to make master patterns for vacuum casting molds.
Both are ideal for making small volumes of finished parts or prototypes. If you need larger quantities, try one of our low volume manufacturing services.
Prototyping To Production
At Djmolding, we also offer low-volume production services where we can provide you with 100,000+ plastic and metal parts. Our low-volume manufacturing options ensure that we can take you through the entire journey from prototype to bridge tooling to low-volume production. Learn more about the benefits of manufacturing in low volumes.
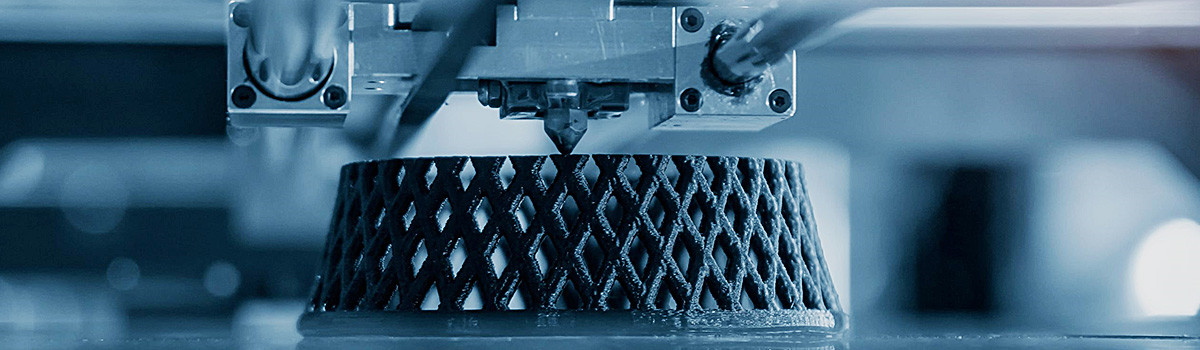
Rapid prototyping is a process that allows designers and engineers to quickly produce physical models of their designs. It is a crucial step in product development, enabling designers to test and refine their ideas before committing to costly manufacturing processes. Rapid prototyping services have become increasingly popular in recent years as technological advances have made the process faster, more accurate, and more affordable than ever before.
What is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is a process used to quickly produce physical models of a design using computer-aided design (CAD) software and various manufacturing technologies. This process allows designers and engineers to test and refine their ideas before moving forward with costly production processes.
Traditionally, creating a prototype was a time-consuming and expensive process. It involved creating a hand-made physical model, often using clay or foam. This process could take weeks or even months, and making changes to the prototype required starting over from scratch.
With rapid prototyping, the process is much faster and more efficient. CAD software is used to create a 3D model of the design, which is then sent to a 3D printer or other manufacturing technology to create a physical model. The process can be completed in a matter of hours or days, depending on the complexity of the design.
The Importance of Prototyping in Product Development
Prototyping is an essential step in the product development process. It allows designers and engineers to create physical models of their designs, which can be used to test and refine the product before it goes into production. There are several reasons why prototyping is so important in product development:
- Testing and Refinement: Prototyping allows designers to test the functionality and performance of their product in a real-world environment. This can help to identify any flaws or areas for improvement, which can be addressed before the product goes into production.
- Cost Savings: Prototyping can help identify design flaws or manufacturing errors early in the development process, saving time and money in the long run. It is much less expensive to make changes to a prototype than to make changes to a product that has already been manufactured.
- Communication and Collaboration: Prototyping allows designers, engineers, and other stakeholders to visualize the product in a tangible way, which can help to facilitate communication and collaboration. It is much easier to discuss a physical prototype than a design on paper or in a digital format.
- Iterative Design Process: Prototyping allows for an iterative design process in which designers can create multiple product versions and test each to see which works best. This process can lead to a better end product, as designers can refine the design based on feedback from each iteration.
- Customer Feedback: Prototyping allows designers to get feedback from customers or end-users, which can be used to refine the product and ensure that it meets the needs and expectations of its intended audience.
Traditional Prototyping vs. Rapid Prototyping
Traditional and rapid prototyping are two different approaches to creating physical design models in product development. Here are some of the key differences between the two:
- Time: Traditional prototyping can be time-consuming, as it often involves creating a physical model by hand. This process can take weeks or even months. On the other hand, rapid prototyping can be completed in a matter of hours or days, depending on the complexity of the design.
- Cost: Traditional prototyping can also be more expensive than rapid prototyping, as it often involves using costly materials and requires skilled labor to create the physical model. Rapid prototyping is generally more affordable, using digital technologies like 3D printing to create the physical model.
- Iteration: With traditional prototyping, changing the physical model can be difficult and time-consuming, as it may require starting over from scratch. With rapid prototyping, changes to the digital model can be made quickly and easily, allowing for a more iterative design process.
- Accuracy: Traditional prototyping can be more accurate than rapid prototyping, allowing for more precise control over the materials and construction process. However, rapid prototyping has become increasingly accurate in recent years, with technological advances allowing for higher resolution and greater accuracy in the physical models produced.
- Materials: Traditional prototyping often uses a broader range of materials than rapid prototyping, including materials like clay or foam that may be difficult to replicate with digital technologies. However, rapid prototyping has the advantage of using a wide range of digital materials, including plastics, metals, and composites.
How Rapid Prototyping Works
Rapid prototyping is a process used to quickly produce physical models of a design using computer-aided design (CAD) software and various manufacturing technologies. Here’s how the process works:
- Design: The first step in rapid prototyping is to create a 3D model of the invention using CAD software. The designer can use the software to create a digital product model with all the necessary details and specifications.
- Preparation: The digital file is prepared for rapid prototyping once the design is complete. This involves converting the CAD file into a format that can be read by the specific manufacturing technology that will be used to create the physical model.
- Printing: The next step is to use a 3D printer or other rapid prototyping technology to create the physical model. The printer reads the digital file and uses it to build up the physical model layer by layer, using materials like plastic, metal, or even ceramics.
- Post-Processing: Once the physical model is created, it may require some post-processing to remove excess material or smooth out rough edges. This may involve using sandpaper or other tools to clean up the model and prepare it for testing or further refinement.
- Testing: Once the physical model is complete, it can be tested to ensure that it meets the specifications and functions as intended. This may involve testing the model in a real-world environment or using simulated testing methods.
- Refinement: The design may need to be refined or modified based on the testing results. This is where rapid prototyping shines, as the digital file can be easily modified, and a new physical model can be printed quickly and easily, allowing for an iterative design process that can help ensure the final product is as good as possible.
Types of Rapid Prototyping Technologies
Rapid prototyping technologies are used to create physical models of a design quickly and efficiently. There are several types of rapid prototyping technologies, each with strengths and weaknesses. Here are some of the most common types:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM is a 3D printing technology that extrudes a thin layer of melted plastic material onto a build platform, layer by layer, to create a physical model. FDM is one of the most common rapid prototyping technologies, as it is relatively inexpensive and can produce models quickly.
- Stereolithography (SLA): SLA is a rapid prototyping technology that uses a UV laser to cure a liquid photopolymer resin into a solid part. The resin is cured layer by layer, each built on top of the previous one to create the final model. SLA is known for producing highly accurate and detailed models but can be more expensive than other rapid prototyping technologies.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS is a 3D printing technology that uses a laser to selectively fuse layers of powdered material, such as plastic or metal, together to create a physical model. SLS can create highly detailed and complex models but can be more expensive than other rapid prototyping technologies.
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): DMLS is a rapid prototyping technology that uses a high-powered laser to melt and fuse the metal powder to create a physical model. DMLS is commonly used in the aerospace and automotive industries to develop high-strength metal parts.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): DLP is a rapid prototyping technology that uses a digital light projector to selectively cure a liquid photopolymer resin into a solid part. DLP is known for producing highly detailed and accurate models but can be more expensive than other rapid prototyping technologies.
- Binder Jetting: Binder Jetting is a rapid prototyping technology that works by selectively depositing a liquid binder onto a powdered material, layer by layer, to create a physical model. Once the model is complete, it is sintered in a furnace to form a solid part. Binder Jetting is commonly used to make sand molds for casting metal parts.
Advantages of Rapid Prototyping Services
Rapid prototyping services offer designers, engineers, and manufacturers many advantages in product development. Here are some of the key benefits of using fast prototyping services:
- Speed: The most significant advantage of rapid prototyping services is speed. With traditional prototyping methods, it can take weeks or even months to create a physical model of a design. On the other hand, fast prototyping services can produce a physical model in a matter of days, allowing designers to test and refine their ideas much more quickly.
- Cost savings: Rapid prototyping services can also save money in product development. By quickly producing physical models, designers can identify and correct design flaws early on, reducing the likelihood of expensive changes during the manufacturing process. Additionally, rapid prototyping can lessen the need for expensive tooling and molds, as the physical models can be produced directly from a digital file.
- Iterative design: Rapid prototyping services allow for an iterative design process, where designers can quickly change a design and produce a new physical model to test. This can lead to a more refined and optimized final design as issues are identified and resolved early in product development.
- Customization: Rapid prototyping services enable the creation of customized and personalized products. With traditional manufacturing methods, producing unique products in small quantities can be difficult and expensive. Rapid prototyping services, on the other hand, can produce highly customized products quickly and cost-effectively.
- Improved communication: Rapid prototyping services allow designers and manufacturers to communicate more effectively about the design of a product. With a physical model in hand, stakeholders can better understand the structure and provide feedback, leading to a more collaborative and productive design process.
- Risk reduction: Rapid prototyping services can help reduce product failure risk. By quickly producing and testing physical models, designers can identify and correct potential issues before moving on to production. In the long run, this can save time and money, as product failures can be expensive to rectify.
- Faster time to market: Rapid prototyping services can speed up the time to market for a product. By quickly producing physical models and refining the design, manufacturers can move from concept to production more quickly, giving them a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
- Enhanced design quality: Rapid prototyping services can improve the quality of the final product design. By quickly producing and testing physical models, designers can identify and correct design flaws early in the process, resulting in a more refined and optimized final product.
- More creativity: Rapid prototyping services can encourage creativity in the design process. With the ability to quickly produce physical models, designers can experiment with different designs and ideas without fear of costly mistakes.
Disadvantages of Rapid Prototyping Services
While there are many advantages to using rapid prototyping services, there are also some potential disadvantages to consider:
- Limited Material Properties: Although rapid prototyping technologies have improved dramatically over the years, there are still limitations in the types of materials that can be used for prototyping. While some service providers offer a range of materials, there may be limitations in the material properties, such as strength, durability, or thermal resistance.
- Surface Finish and Quality: Rapid prototyping methods may produce different surface finish and quality than traditional manufacturing methods. In some cases, additional finishing processes may be required to achieve the desired surface finish or texture, which can add time and cost to the project.
- Size and Complexity Limitations: Rapid prototyping is generally best suited for small to medium-sized parts with moderate complexity. Large or complex functions may be difficult or time-consuming to produce with rapid prototyping technologies, limiting the design possibilities.
- Cost: While rapid prototyping can save money in the long run by detecting design flaws early in the process, the initial cost of prototyping can be high, particularly for larger or more complex designs. The cost of materials, equipment, and labor can add up quickly, particularly if multiple iterations are required.
- Not Suitable for Mass Production: Rapid prototyping technologies are designed for small-scale production and must be better suited for mass production. Once the design has been finalized and validated through prototyping, it may be necessary to transition to a different manufacturing process to produce large quantities at a lower cost.
- Limitations in Accuracy and Precision: While rapid prototyping technologies have improved accuracy and precision, there may still be limitations in achieving the exact tolerances required for specific applications. This can be particularly challenging for parts that need tight tolerances or complex geometries.
- Environmental Concerns: Rapid prototyping technologies typically require various chemicals and materials that can be hazardous to the environment if not correctly disposed of. Service providers must follow appropriate waste disposal protocols to minimize the environmental impact.
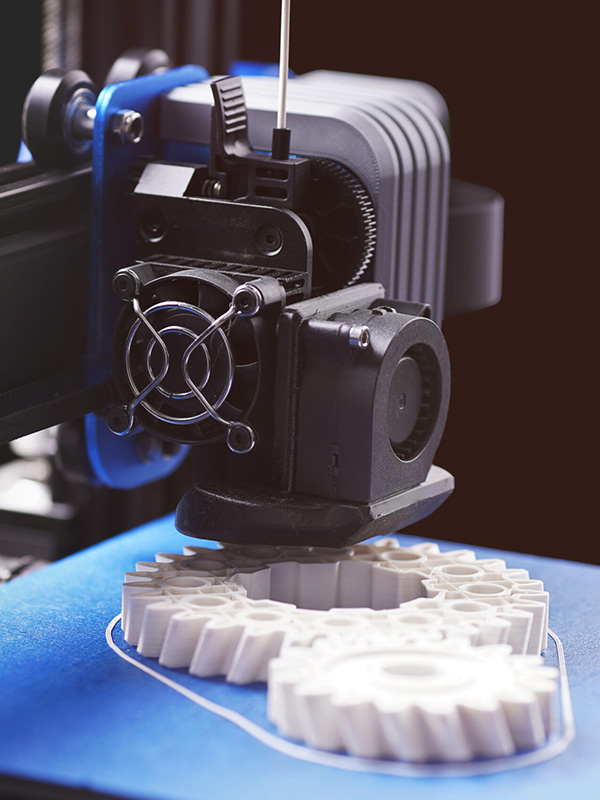

Cost Savings with Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping can offer significant cost savings in the product development process. One of the main ways it can save costs is by reducing the need for expensive tooling and molds. With traditional manufacturing methods, the production of tooling and molds can be time-consuming and costly. However, with rapid prototyping, physical models can be produced directly from a digital file, eliminating the need for tooling and molds altogether. This saves time and money and allows for more flexibility in design changes and iterations.
Additionally, rapid prototyping can help to identify design flaws early on in the product development process, reducing the likelihood of expensive changes during the manufacturing process. By quickly producing and testing physical models, designers can identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments before moving on to production. In the long run, this can save significant time and money, as product failures can be expensive to rectify.
Furthermore, rapid prototyping allows for producing small quantities of customized and personalized products at a lower cost. Creating unique products in small amounts with traditional manufacturing methods can be difficult and expensive. However, rapid prototyping services can produce highly customized products quickly and cost-effectively. This can be especially beneficial for businesses making small batches of customized products or prototypes for testing and validation.
Time Savings with Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping offers significant time savings in the product development process. With traditional prototyping methods, it can take weeks or even months to produce a physical model of a design. However, with rapid prototyping, a physical model can be made in a matter of days or even hours, depending on the complexity of the invention. This can significantly reduce the time it takes to move from concept to production, allowing businesses to get their products to market faster.
Furthermore, rapid prototyping enables an iterative design process, where designers can quickly change a design and produce a new physical model to test. This allows for faster feedback and stakeholder collaboration, leading to a more refined and optimized final design. This iterative process can be repeated multiple times quickly, allowing for rapid design iterations and reducing the overall time it takes to develop a product.
Additionally, rapid prototyping can reduce the time it takes to identify and correct design flaws. By quickly producing and testing physical models, designers can identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments before moving on to production. This can significantly reduce the time it takes to rectify design issues, which can be time-consuming and expensive in manufacturing.
Better Communication and Collaboration with Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping offers several advantages when it comes to communication and collaboration in the product development process. Producing physical models quickly and accurately, rapid prototyping can facilitate better communication and collaboration between designers, engineers, stakeholders, and customers.
Firstly, rapid prototyping allows for the production of physical models that can be used to communicate design concepts and ideas to others. Instead of relying on 2D drawings or computer renderings, designers can produce physical models that stakeholders can touch, feel, and interact with. This helps bridge the gap between designers and non-technical stakeholders, making it easier for everyone to understand and visualize the design.
Secondly, rapid prototyping enables an iterative design process where designers can quickly change a design and produce a new physical model to test. This allows for faster feedback and stakeholder collaboration, leading to a more refined and optimized final design. Rapid prototyping can also help identify potential issues or areas for improvement early on in the product development process, leading to more effective collaboration and decision-making.
Thirdly, rapid prototyping allows for the production of customized and personalized products, which can be tailored to specific customer needs and preferences. This can be especially beneficial for businesses producing small batches of customized products or prototypes for testing and validation. Companies can foster better communication and collaboration by involving customers in the design process and creating personalized products, leading to more satisfied and loyal customers.
Improved Quality and Functionality with Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping offers several advantages when it comes to improving the quality and functionality of products. By enabling an iterative design process, rapid prototyping can help identify and rectify design flaws early in the product development process, leading to a better final product. Additionally, by producing physical models that can be tested and validated, rapid prototyping can help improve product functionality, ensuring that they meet the needs and expectations of customers.
One key advantage of rapid prototyping is that it enables an iterative design process. By quickly producing and testing physical models, designers can identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments before moving on to production. This can significantly reduce the likelihood of design flaws or errors in the final product, leading to a higher-quality final product.
Another advantage of rapid prototyping is that it produces physical models that can be tested and validated for functionality. This helps ensure that products meet the needs and expectations of customers, leading to greater customer satisfaction and loyalty. For example, in the automotive industry, rapid prototyping produces physical models of car parts that can be tested for strength, durability, and other functional characteristics. By trying these parts early in the product development process, designers can make necessary adjustments to improve their functionality before moving on to production.
In addition to enabling an iterative design process and improving the functionality of products, rapid prototyping can also help to improve the overall quality of products. By producing physical models that can be inspected and tested for defects, designers can identify and rectify quality issues early in product development. This helps ensure that the final product is of high quality, meets customer expectations, and is less likely to experience quality-related issues in the field.
Iterative Design Process with Rapid Prototyping
The iterative design process is a crucial advantage of rapid prototyping, allowing designers to quickly create and test multiple iterations of a product design before moving on to production. This process involves creating a prototype, testing it, and then making necessary adjustments based on feedback before repeating the cycle until a final design is achieved. By using rapid prototyping to facilitate this process, designers can reduce the time and cost associated with traditional design processes while improving the final product’s quality and functionality.
The iterative design process with rapid prototyping typically involves several key steps. The first step is to create a preliminary design using computer-aided design (CAD) software or another design tool. This design is then used to create a physical prototype using rapid prototyping technology. Once the prototype is made, it is tested to identify any design flaws or areas for improvement.
Based on the initial testing results, the designer will make necessary adjustments to the design using CAD software or other design tools. The updated design is then used to create a new physical prototype, which is tested again to identify further issues or improvement areas. This cycle of testing and adjusting the design continues until the final product meets the desired specifications.
The use of rapid prototyping technology in this process offers several benefits over traditional design processes. For one, it allows for a much faster turnaround time, as physical prototypes can be produced in hours rather than weeks or months. This will enable designers to quickly test and refine multiple iterations of a design, helping to improve the final product and reduce the time to market.
Another advantage of using rapid prototyping in the iterative design process is that it allows for greater collaboration between designers, engineers, and other stakeholders. By producing physical prototypes that can be touched, tested, and evaluated, stakeholders can provide more informed feedback on the design, leading to better decision-making and more effective collaboration.
Early Detection of Design Flaws with Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping allows for the early detection of product design flaws, which is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets the desired specifications and quality standards. Design flaws can range from minor issues, such as aesthetic flaws, to significant defects, such as structural weaknesses, that could compromise the safety and reliability of the final product. By using rapid prototyping to create physical models of products, designers can identify these flaws early in the product development process, allowing them to make necessary adjustments and improvements before moving on to production.
The early detection of design flaws is possible because rapid prototyping allows for the creation of physical models quickly and inexpensively. It can take weeks or even months to create physical prototypes using traditional manufacturing methods in conventional design processes, and this can make it difficult to test multiple design iterations and identify potential design flaws early in product development. However, with rapid prototyping, physical prototypes can be produced in hours, allowing designers to quickly test and refine multiple design iterations and identify potential flaws before they become more complex and expensive.
Once a physical prototype has been produced using rapid prototyping, it can be evaluated for potential design flaws utilizing various methods, including visual inspection, material testing, and computer simulations. Visual inspection can help to identify aesthetic defects and other surface-level issues that may not be immediately apparent using different methods. Physical testing can help to identify structural weaknesses and other problems related to the functionality and durability of the product. Computer simulations can help predict a product’s performance under various conditions and identify potential design flaws that may take time to be apparent through other methods.
By identifying design flaws early in the product development process, designers can make necessary adjustments and improvements to the design, reducing the likelihood of these flaws making their way into the final product. This helps ensure that the final product meets the desired specifications and quality standards, improving customer satisfaction and reducing the likelihood of outcome recalls or other quality-related issues.
Reduced Risk of Manufacturing Errors with Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping can significantly reduce the risk of manufacturing errors in product development. Traditional manufacturing methods often involve complex and expensive tooling and molds, leading to high costs and risks if mistakes occur during manufacturing. By using rapid prototyping to create physical models of products, designers can test and refine their designs before committing to costly tooling and manufacturing processes.
Rapid prototyping allows for creating physical prototypes quickly and inexpensively, enabling designers to test multiple design iterations and identify potential issues before moving on to production. This iterative process can help to refine the design and reduce the risk of errors during manufacturing.
In addition, rapid prototyping allows for using various materials, including plastics, metals, and composites. This enables designers to test the functionality and durability of their designs using materials similar to those used in the final product. By doing so, they can identify potential issues related to the manufacturing process and make necessary adjustments to reduce the risk of errors and defects.
Rapid prototyping can also reduce the risk of errors by allowing designers to test the product in real-world conditions. Using physical prototypes, designers can subject their designs to various stresses and loads, including temperature changes, vibration, and impact. This enables them to identify potential issues that may need to be apparent through computer simulations or other testing methods.
Finally, rapid prototyping allows for identifying errors and issues before the manufacturing process begins. This can help reduce the risk of costly mistakes and defects during the manufacturing process, leading to product recalls, wasted materials, and other expenses.
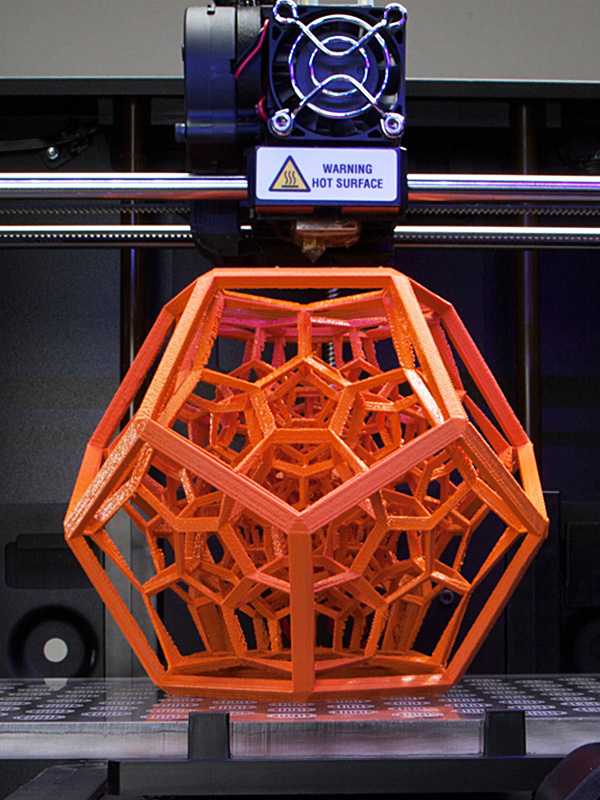
Streamlined Product Development with Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping has revolutionized product development by providing a streamlined approach to creating and testing new products. This process enables designers and engineers to quickly and efficiently test their ideas, make adjustments, and get products to market faster than ever before. Here are some ways in which rapid prototyping can help streamline product development:
- Faster design iteration: With rapid prototyping, designers can create and test multiple design iterations quickly and inexpensively. This enables them to refine their designs and make adjustments based on customer or stakeholder feedback, ultimately resulting in a better end product.
- Reduced time to market: Rapid prototyping allows for faster development times, which means products can be brought to market sooner. This can be especially important in industries with high competition or rapidly changing technologies.
- Better collaboration: Rapid prototyping enables collaboration between designers, engineers, and other stakeholders. By creating physical prototypes, everyone involved in the project can get a better sense of the product, provide feedback, and make suggestions for improvement.
- Improved quality: Rapid prototyping allows for testing the product in real-world conditions, enabling designers to identify potential issues before manufacturing begins. This can improve the overall quality of the final product and reduce the likelihood of costly errors or defects.
- Reduced costs: Rapid prototyping can reduce the overall costs of product development by identifying potential issues early in the process. By doing so, designers can make adjustments before committing to expensive tooling and manufacturing processes.
- Increased customization: Rapid prototyping enables designers to create customized products quickly and easily. This can be especially valuable in industries such as healthcare, where personalized products are becoming increasingly important.
- Better market testing: Rapid prototyping can help designers test products in the market quickly and inexpensively. By creating physical prototypes and soliciting customer feedback, designers can identify potential issues and make adjustments before committing to large-scale manufacturing.
Flexibility in Design Changes with Rapid Prototyping
One of the critical advantages of rapid prototyping is its flexibility in accommodating design changes during the product development process. Traditional prototyping methods, such as injection molding or CNC machining, can be time-consuming and costly to modify once tooling is created. In contrast, rapid prototyping technologies allow for quick and easy modifications to be made to the design.
Here are some ways in which rapid prototyping allows for flexibility in design changes:
- Quick and easy iterations: With rapid prototyping, designers can create multiple design iterations quickly and inexpensively. This allows immediate changes to be made and tested, reducing the time and cost of traditional prototyping methods.
- Reduced tooling costs: Traditional prototyping methods require expensive tooling to be created before any design changes can be made. Rapid prototyping eliminates the need for costly tooling, allowing modifications to be made on the fly.
- Simplified design process: Rapid prototyping technologies allow 3D models to be created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This simplifies the design process and allows for quick and easy modifications to be made.
- Enhanced collaboration: Rapid prototyping enables designers and other stakeholders to collaborate more effectively on the design process. By creating physical prototypes, everyone involved can better understand the product and provide feedback for improvements.
- Improved product quality: By allowing for design changes to be made quickly and easily, rapid prototyping can improve the overall quality of the final product. Testing and modifying designs in real-world conditions can help to identify potential issues and ensure that the final product meets customer expectations.
- Increased customization: Rapid prototyping enables designers to create customized products quickly and easily. This can be especially valuable in industries such as healthcare, where personalized products are becoming increasingly important.
Customization and Personalization with Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping technologies have revolutionized how products can be customized and personalized for individual customers. The ability to quickly and easily create prototypes using 3D printing, CNC machining, and other rapid prototyping techniques has opened up new possibilities for customization in various industries, from healthcare to consumer goods.
Here are some ways in which rapid prototyping enables customization and personalization:
- Customized product design: Rapid prototyping allows designers to create custom product designs quickly and easily. This can be especially valuable in industries such as healthcare, where personalized products are becoming increasingly important.
- Personalized fit and function: Rapid prototyping makes it possible to create products that fit and function perfectly for individual customers. This can include customized medical implants, sports equipment tailored to an athlete’s unique needs, or even custom-made jewelry.
- Fast and efficient customization: Rapid prototyping technologies allow for quick and efficient customization of products. Companies can offer personalized products without significant time or cost penalties.
- Low-volume production: Rapid prototyping can produce low volumes of customized products at a relatively low cost. This makes it possible to offer customers personalized products without investing in expensive tooling or production equipment.
- Improved customer experience: Personalized products can improve the customer experience by making them feel more valued and engaged with the product. This can lead to increased customer loyalty and repeat business.
- Enhanced brand differentiation: Customized products can help companies to differentiate themselves from competitors and stand out in crowded markets. By offering personalized products, companies can appeal to customers looking for unique and tailored products.
Access to Advanced Materials with Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping technologies have enabled access to advanced materials that were previously difficult or expensive to work with. This has opened up new possibilities for product design and innovation in various industries, from aerospace to biomedical engineering.
Here are some ways in which rapid prototyping enables access to advanced materials:
- Testing of new materials: Rapid prototyping allows designers to test and evaluate new materials quickly and easily. This can help to identify promising new materials for use in product development and enable companies to stay ahead of the curve in terms of material innovation.
- Customized material properties: Rapid prototyping can create parts with specific material properties, such as strength, flexibility, or thermal resistance. This means that companies can tailor their products to meet specific performance requirements.
- Using exotic materials: Rapid prototyping enables using exotic materials, such as titanium, carbon fiber, and ceramics, that were previously difficult or expensive to work with. This has opened up new possibilities for product design in industries such as aerospace and defense.
- Reduced waste: Rapid prototyping technologies enable precise control over material usage, reducing waste and minimizing the environmental impact of product development.
- Lower cost: Access to advanced materials through rapid prototyping can be cheaper than traditional manufacturing methods. Companies can experiment with new materials and innovate more freely without incurring high costs.
- Improved performance: Using advanced materials and customized material properties, products can be designed with enhanced performance characteristics, such as increased strength, reduced weight, or improved durability.
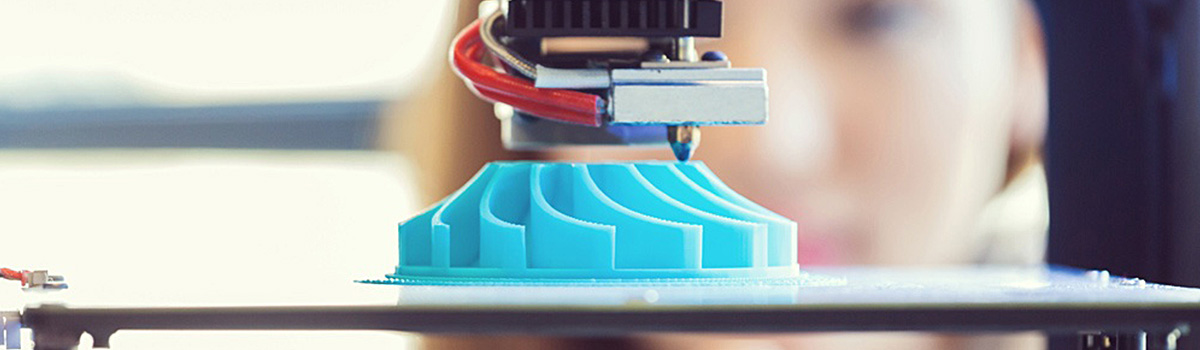
Fast Turnaround Time with Rapid Prototyping Services
One of the critical advantages of rapid prototyping services is the ability to provide fast turnaround times. This is because rapid prototyping technologies use computer-controlled processes to quickly create physical prototypes of a product design. Here are some ways in which immediate prototyping services provide fast turnaround times:
- Quick prototyping process: Rapid prototyping technologies use automated processes to create physical models of a design. This eliminates manual labor and significantly reduces the time required to develop a prototype.
- Shorter lead times: Traditional manufacturing methods can require significant tooling, setup, and production lead times. With rapid prototyping services, however, there is no need for tooling or design, which reduces lead times and speeds up the prototyping process.
- Rapid design iterations: Rapid prototyping services enable designers to quickly iterate on a design, making changes and adjustments in real time. This enables faster testing and validation of a plan, accelerating the overall product development process.
- Simultaneous design and prototyping: Rapid prototyping services make it possible to design and prototype a product simultaneously. This means that designers can test out different design concepts and make changes as needed without waiting for a physical prototype to be created.
- Faster testing and validation: Rapid prototyping services provide quick turnaround times for the testing and validating of a product design. This allows designers to identify and address design flaws or issues early in the development process, reducing the need for costly and time-consuming rework later on.
- Shorter time to market: The fast turnaround times provided by rapid prototyping services can help companies bring products to market more quickly. This can be a significant competitive advantage, as companies that can get their products to market faster are more likely to capture market share and generate revenue sooner.
Applications of Rapid Prototyping Services
Rapid prototyping services have various applications in various industries, from aerospace and automotive to medical devices and consumer electronics. Here are some of the most common applications of rapid prototyping services:
- Concept modeling: Rapid prototyping services can create physical models of new product designs for testing and evaluation. These models help designers and engineers visualize their ideas and make design changes quickly.
- Functional prototyping: Rapid prototyping services can create fully functional prototypes that can be tested for functionality, durability, and other factors. This can help designers and engineers validate their designs and identify potential problems early in development.
- Tooling: Rapid prototyping services can create tooling and molds for manufacturing processes such as injection molding, die casting, and sheet metal forming. These tools can be made quickly and accurately, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional tooling methods.
- Production parts: Rapid prototyping services can create low-volume production parts quickly and cost-effectively. This can be particularly useful for companies producing small quantities of custom or specialized functions.
- Medical devices: Rapid prototyping services are commonly used in the medical device industry to create prototypes for testing and evaluation. This includes surgical instruments, prosthetics, and implants.
- Aerospace and automotive: Rapid prototyping services can be used in the aerospace and automotive industries to create functional prototypes for testing and evaluation. This includes engine parts, structural elements, and interior trim pieces.
- Consumer electronics: Rapid prototyping services can create prototypes for consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, and wearables. This allows designers to test and evaluate new product designs quickly and make changes as needed.
- Architecture: Rapid prototyping services can be used in architecture to create models of buildings and structures for visualization and testing. This includes scale models of buildings and 3D-printed models of building components.
Choosing the Right Rapid Prototyping Service Provider
Choosing the right rapid prototyping service provider is crucial to ensure the successful execution of your product development projects. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a fast prototyping service provider:
- Expertise and Experience: Look for a service provider with knowledge and experience in the specific industry or field relevant to your project. They should have a track record of successfully delivering high-quality prototypes in your industry and be familiar with the unique requirements and challenges it entails.
- Technologies and Capabilities: Evaluate the range of rapid prototyping technologies and capabilities the service provider offers. Ensure they have the right equipment and expertise to handle your specific project requirements, whether it involves 3D printing, CNC machining, injection molding, or other techniques.
- Material Options: Consider the range of materials available for prototyping. A reputable service provider should offer a variety of materials suitable for your application, including plastics, metals, composites, or specialized materials relevant to your industry.
- Quality Assurance: Assess the service provider’s quality control processes to ensure that they maintain high standards throughout the prototyping process. Ask about their inspection and testing procedures to ensure the prototypes’ accuracy, precision, and functionality.
- Speed and Turnaround Time: Rapid prototyping is known for its fast turnaround times, but different service providers may have varying production capacities and lead times. Evaluate their production capacity and ability to meet your project timeline requirements.
- Cost and Pricing Structure: Obtain detailed pricing information from the service provider, including setup fees, material costs, and additional charges for design modifications or post-processing. Compare pricing structures from different providers to ensure a fair and cost-effective solution.
- Design Assistance and Support: Consider whether the service provider offers design assistance and support. An experienced provider can provide valuable insights and suggestions to optimize your design for prototyping and production.
- Customer Reviews and References: Read customer reviews and testimonials, or ask for references from previous clients. This can provide insights into the service provider’s reliability, responsiveness, and overall customer satisfaction.
- Confidentiality and Intellectual Property Protection: Ensure the service provider has protocols to protect your confidential information and intellectual property rights. A non-disclosure agreement (NDA) may be necessary to safeguard your proprietary designs and ideas.
- Customer Service and Communication: Evaluate the service provider’s responsiveness, communication channels, and customer service. A reliable provider should be accessible and responsive to your inquiries, providing clear and timely communication throughout the prototyping process.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select a rapid prototyping service provider that aligns with your project requirements, budget, and quality expectations. Collaboration with a trusted provider will contribute to the successful realization of your prototypes and bring you closer to achieving your product development goals.
In conclusion, rapid prototyping services have revolutionized the product development process by allowing designers and engineers to quickly and cost-effectively create physical prototypes of their designs. With the many advantages of rapid prototyping, it has become an essential step in product development for businesses of all sizes and industries. By partnering with a reliable and experienced quick prototyping service provider, companies can bring their ideas to life faster, with greater accuracy and functionality, and at a lower cost.



