Two Plate Mold Vs. Three Plate Mold: What’s Their Difference?
Two Plate Mold Vs. Three Plate Mold: What’s Their Difference?
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process for producing plastic parts. Among the critical components in this process are the molds themselves. Two of the most common types of molds are two-plate molds and three-plate molds. Each has its unique features, advantages, and applications. Understanding the differences between these two mold types is crucial for selecting the right one for a specific manufacturing need.

Introduction to Injection Molding
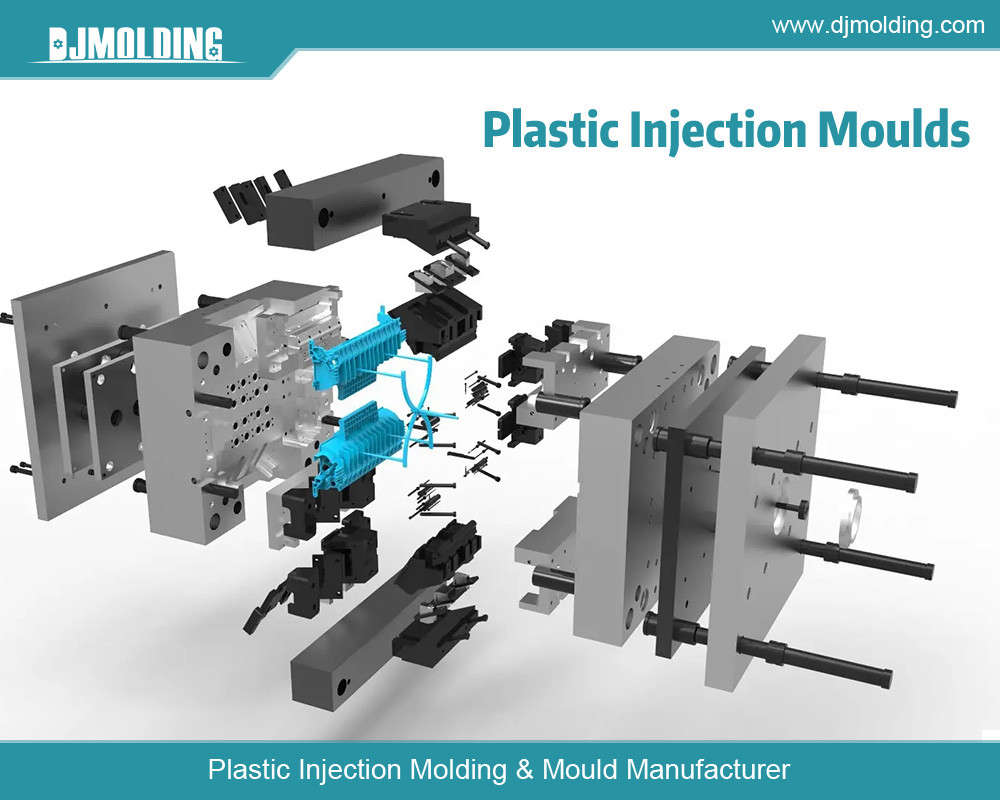
Injection molding involves injecting molten plastic material into a mold cavity, which cools and solidifies into the desired shape. The mold, which consists of two or more plates, is a critical element in determining the quality, cost, and speed of production. The essential components of an injection mold include:
- Cavity and Core: The cavity is part of the mold that shapes the exterior of the part, while the core shapes the interior.
- Sprue: The channel through which the molten plastic enters the mold.
- Runner System: Channels that distribute the molten plastic to various cavities within the mold.
- Gates: Small openings through which the molten plastic enters the cavity.
The design of the mold, including the number of plates, significantly influences these components and, consequently, the final product.
Overview of Two Plate Molds
A two-plate mold is the most basic and widely used type of injection mold. It consists of two main plates:
- Fixed Plate (A-side): This plate is attached to the stationary part of the injection molding machine and contains the sprue through which the plastic material is injected.
- Moving Plate (B-side): This plate is attached to the machine’s movable part and moves back and forth during the molding process.
When the mold is closed, the cavity and core come together to form the part’s shape. After the plastic has been injected and cooled, the mold opens, and the part is ejected.
Key Features of Two Plate Molds
- Simple Design: The two-plate mold is straightforward, making it easy to manufacture and maintain.
- Cost-Effective: Due to their simplicity, two-plate molds are generally less expensive to produce than more complex molds.
- Suitable for Simple Parts: This mold type is ideal for producing simple parts with a single gate.
- Gate Location: The gate is usually located at the edge of the part, which can sometimes lead to imperfections like weld lines.
Applications of Two Plate Molds
Two-plate molds are commonly used in applications where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are prioritized. They are ideal for producing parts with a basic geometry, such as:
- Household items (e.g., containers, lids)
- Automotive components
- Toys
- Simple electronic housings
The two-plate mold is favored in high-volume production settings where the part’s design allows for efficient manufacturing without additional complexity.
Overview of Three Plate Molds
A three-plate mold is more complex than a two-plate mold, consisting of three main plates:
- Fixed Plate (A-side): Similar to the two-plate mold, this plate is attached to the stationary part of the machine.
- Movable Plate (B-side): This plate is connected to the moving part of the machine.
- Runner Plate: A third plate that separates the sprue and runner system from the part.
In a three-plate mold, the runner system is located between the fixed and movable plates. When the mold opens, the runner plate moves separately, allowing the part and the runner system to be ejected independently. This design allows for more complex gating systems, such as multiple gates or gates located at the center of the part.
Key Features of Three Plate Molds
- Complex Design: The three-plate mold’s design is more intricate, allowing for greater flexibility in gate placement.
- Improved Part Quality: With the ability to place gates in optimal locations, three-plate molds can produce parts with fewer imperfections, such as weld lines or voids.
- Suitable for Complex Parts: This mold type is ideal for producing complex parts that require multiple gates or intricate runner systems.
- Higher Cost: Due to the added complexity, three-plate molds are generally more expensive to manufacture and maintain.
Applications of Three Plate Molds
Three-plate molds are commonly used in applications where part quality and complexity are more critical than cost. They are ideal for producing parts with complex geometries, such as:
- Precision automotive components
- Medical devices
- Complex electronic housings
- Multi-cavity molds for small parts
The three-plate mold is often used in industries where the highest quality and precision are required, and the added cost is justified by the benefits in part performance.
Detailed Comparison: Two-Plate Mold vs. Three-Plate Mold
To fully understand the differences between two-plate and three-plate molds, it’s essential to compare them across several critical factors:
Design Complexity
- Two Plate Mold: The design is straightforward, with just two main plates. This simplicity makes it easier to manufacture, assemble, and maintain.
- Three Plate Mold: Adding a third plate introduces complexity, especially in the runner system. This complexity requires more precise engineering and increases the mold manufacturing time and cost.
Gate Location and Part Quality
- Two Plate Mold: The gate is typically located at the edge of the part, which can lead to cosmetic defects such as weld lines or flow marks. This placement may also limit the design options for the part.
- Three Plate Mold: The gate can be placed anywhere on the part, including in the center. This flexibility allows for better material flow control, producing higher part quality with fewer defects.
Cost Considerations
- Two Plate Mold: Generally less expensive to produce and maintain, making it the preferred choice for high-volume production of simple parts.
- Three Plate Mold: The added complexity and precision required for a three-plate mold result in higher manufacturing and maintenance costs. However, this cost is often justified by the improved part quality and flexibility in design.
Production Speed
- Two Plate Mold: Faster to operate due to its simplicity, making it ideal for high-speed production environments.
- Three Plate Mold: Slightly slower due to the additional steps involved in separating the runner system from the part. However, the impact on overall cycle time is usually minimal.
Maintenance and Durability
- Two-plate mold: This mold is easier to maintain due to its simpler design. Fewer components mean fewer potential points of failure, contributing to its durability.
- Three-plate mold: This mold is more challenging to maintain because of the additional plate and more complex runner system. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure consistent performance and part quality.
Flexibility in Design
- Two Plate Mold: Limited in terms of design flexibility, particularly in gate placement. This limitation can restrict the types of parts that can be produced.
- Three-plate mold offers greater flexibility in part design, including the ability to produce more complex geometries and multi-cavity molds. This flexibility makes it suitable for a broader range of applications.
Choosing Between Two Plate and Three Plate Molds
Selecting the right mold type depends on several factors, including the part’s complexity, production volume, budget, and quality requirements. Here’s a guideline to help in making the decision:
Part Complexity
- Simple Parts: A two-plate mold is usually sufficient for parts with basic geometries and minimal quality requirements.
- Complex Parts: For parts with intricate designs, multiple gates, or high-quality requirements, a three-plate mold is the better choice.
Production Volume
- High Volume: A two-plate mold is typically more suitable for large-scale production where cost efficiency is crucial.
- Low to Medium Volume: A three-plate mold may be more appropriate for smaller production runs if the focus is on quality and flexibility rather than cost.
Budget
- Limited Budget: Two-plate molds are more cost-effective, making them ideal for projects with tight budget constraints.
- Flexible Budget: If the budget allows, investing in a three-plate mold can lead to better part quality and design flexibility, which may offset the higher initial cost in the long run.
Quality Requirements
- Standard Quality: For parts where minor cosmetic defects are acceptable, a two-plate mold will suffice.
- High Quality: A three-plate mold is the preferred option for parts that require the highest quality, with minimal defects and optimal material flow.
Innovations and Trends in Mold Design
The field of injection molding is constantly evolving, with new technologies and innovations shaping the industry. Some trends to watch include:
Advanced Materials
New materials like high-performance plastics and composites are being developed to improve part quality and reduce production costs. These materials often require specialized molds, including both two-plate and three-plate designs.
Automation and Smart Molds
Automation is becoming increasingly prevalent in injection molding. Bright molds incorporate sensors and IoT technology to monitor and optimize production. These advancements can be applied to two-plate and three-plate molds, enhancing their performance and efficiency.
Sustainability
Sustainability is a growing concern in the manufacturing industry, leading to innovations in mold design that reduce waste and energy consumption. Two-plate and three-plate molds can be designed sustainably, using recycled materials and optimizing material flow to minimize waste.
Hybrid Molds
Hybrid molds, combining elements of two-plate and three-plate designs, are emerging as a versatile solution for complex manufacturing needs. These molds offer the simplicity of a two-plate mold with the flexibility and quality advantages of a three-plate mold.
Conclusion
The choice between a two-plate mold and a three-plate mold is not simple, as each has its own advantages and limitations. A two-plate mold is ideal for simple, cost-effective production, while a three-plate mold offers greater flexibility and higher part quality for more complex applications. Understanding the differences between these two mold types is essential for making an informed decision that aligns with the specific needs of a manufacturing project.
As the injection molding industry continues to evolve, innovations in materials, automation, and sustainability will likely influence molds’ design and selection further. Whether choosing a two-plate mold for its simplicity and speed or a three-plate mold for its precision and flexibility, the suitable mold can significantly impact production efficiency, cost, and quality.
For more about two plate mold vs. three plate mold: what’s their difference, you can pay a visit to Djmolding at https://www.djmolding.com/about/ for more info.




