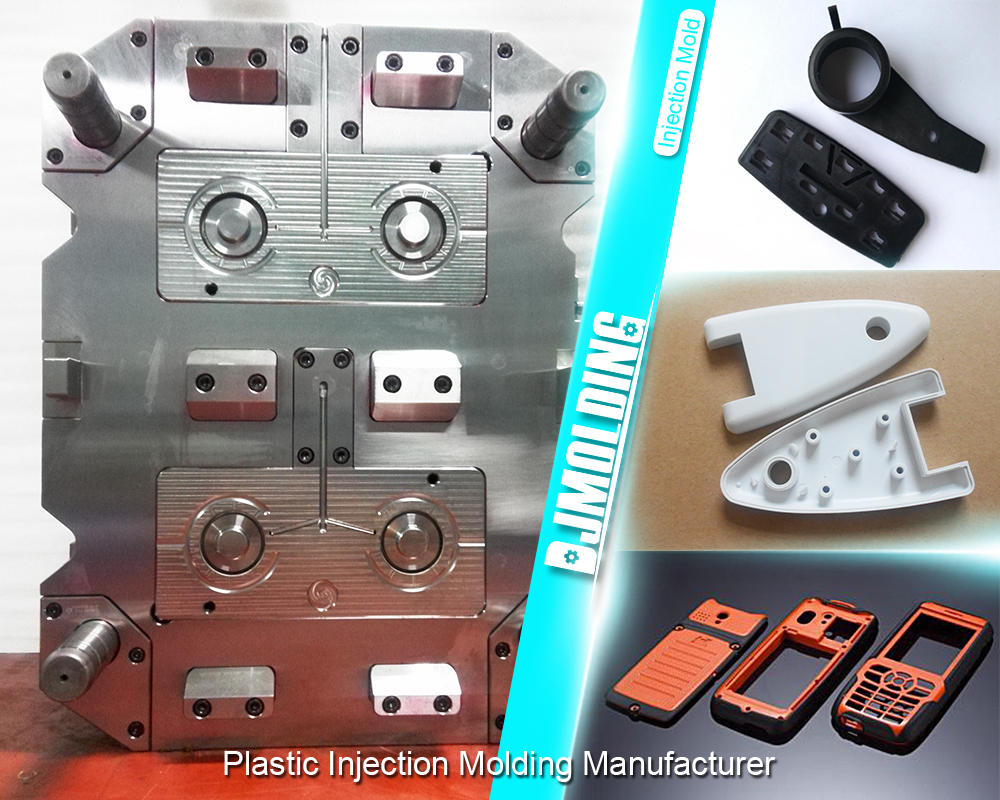
Injection Molding Surface Finish And The Different Types
Injection Molding Surface Finish And The Different Types
Injection molding is a highly versatile and efficient manufacturing process that creates various plastic parts and products. One critical aspect of this process is the surface finish of the molded parts, which significantly impacts their aesthetic quality, functionality, and overall performance. This article delves into the different types of surface finishes achievable through injection molding, exploring their characteristics, applications, and the factors influencing their selection.

Understanding Injection Molding Surface Finish
Injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity to form a specific shape. The surface finish of the molded part is influenced by several factors, including the mold design, material used, and processing conditions. The surface finish quality can range from very smooth and glossy to textured or matte, depending on the intended application and aesthetic requirements.
Key Factors Influencing Surface Finish:
- Mold Material: The type and condition of the mold material play a significant role in determining the surface finish. More complex and more polished mold materials generally produce smoother finishes.
- Mold Design: The design of the mold, including its texture and the presence of any draft angles or parting lines, affects the final surface finish.
- Plastic Material: Different plastic materials have varying flow characteristics and shrinkage rates, impacting the surface texture.
- Processing Conditions: Parameters such as injection pressure, temperature, and cooling time can influence the appearance of the surface finish.
Types of Surface Finishes in Injection Molding
Injection molded parts can exhibit various surface finishes, each suited to different applications and aesthetic preferences. Here, we explore the most common types of surface finishes used in injection molding.
Glossy Finish
A glossy finish is characterized by its shiny, reflective surface. It is often used to enhance a product’s visual appeal. Achieving a glossy finish requires high mold polish and precise processing conditions.
- Characteristics: Smooth, reflective, and highly polished surface.
- Applications: Consumer electronics, automotive trim, and high-end consumer goods.
- Mold Considerations: Requires high-quality, mirror-polished molds to prevent surface defects such as streaks or scratches.
- Challenges: Maintaining a consistent glossy finish can be challenging due to sensitivity to mold imperfections and processing variations.
Matte Finish
A matte finish has a non-reflective, flat appearance. It can reduce glare and provide a sophisticated look. Matte finishes are often achieved by using molds with a textured surface or through post-molding treatments.
- Characteristics: Non-reflective, smooth, or textured surface with a subdued appearance.
- Applications: Industrial parts, consumer goods with a subtle aesthetic, and components requiring reduced glare.
- Mold Considerations: This can be achieved with various textured mold surfaces or secondary finishing processes.
- Challenges: Matte finishes can sometimes reveal mold lines or imperfections more prominently, necessitating careful mold maintenance.
Textured Finish
Textured finishes are designed to create a patterned or embossed surface, which can enhance grip, reduce glare, or provide a unique appearance. Texturing is typically achieved by incorporating patterns into the mold surface.
- Characteristics: Patterns or textures ranging from fine to coarse, depending on the design.
- Applications: Automotive interiors, grips for tools or appliances, and decorative consumer products.
- Mold Considerations: Molds with specific textured patterns are required, which can be complex and costly.
- Challenges: Textured surfaces may trap dirt or require additional cleaning or maintenance.
Sanded Finish
A sanded finish uses abrasive materials to create a uniform, textured surface. This finish is often used for aesthetic purposes or to enhance a product’s tactile feel.
- Characteristics: Uniformly textured surface with a matte appearance, similar to sandblasting.
- Applications: Industrial components, consumer products requiring a tactile surface, and parts with a rugged aesthetic.
- Mold Considerations: Achieved through post-molding processes such as sanding or abrasive blasting.
- Challenges: Post-molding processes can add Time and cost to production, and achieving a uniform finish requires careful control.
High-Gloss Finish
A high-gloss finish is a more intense version of a glossy finish with an exceptionally smooth and reflective surface. It is often used for high-end consumer products where visual appeal is crucial.
- Characteristics: Extremely reflective and smooth, often with a mirror-like quality.
- Applications: Luxury goods, high-end electronics, and premium automotive parts.
- Mold Considerations: Requires meticulous polishing of the mold surface and careful control of processing conditions.
- Challenges: Achieving and maintaining a high-gloss finish can be demanding due to its sensitivity to imperfections and processing variations.
Soft-Touch Finish
A soft-touch finish provides a velvety or rubber-like texture, enhancing the tactile experience of the product. This finish is often used in consumer products where comfort and grip are essential.
- Characteristics: Soft, tactile surface that feels pleasant to the touch.
- Applications: Consumer electronics, ergonomic tools, and high-touch areas in automotive interiors.
- Mold Considerations: Typically achieved through specialized mold coatings or materials that impart a soft texture.
- Challenges: Maintaining the consistency of the soft-touch finish can be challenging, especially in high-volume production.
Metallic Finish
A metallic finish imparts a metallic look to the molded part, often achieved through metallic pigments or coatings. This finish provides a premium appearance and can mimic the look of metal.
- Characteristics: Shiny, metallic appearance with a reflective quality.
- Applications: Decorative components, automotive parts, and high-end consumer products.
- Mold Considerations: Metallic pigments or coatings, which can be applied during or after molding, are required.
- Challenges: Achieving a consistent metallic finish can be challenging due to the need for precise pigment distribution and application techniques.
Factors Influencing Surface Finish Selection
Selecting the appropriate surface finish for an injection molded part involves considering several factors:
Functional Requirements
The intended function of the part often dictates the choice of surface finish. For instance, parts requiring high grip or friction may benefit from a textured finish, while components with aesthetic requirements might call for a glossy or metallic finish.
Aesthetic Preferences
Aesthetic considerations are crucial in surface finish selection, especially for consumer-facing products. Depending on the design goals, the part’s visual appeal can be enhanced through finishes like high-gloss, matte, or metallic.
Cost and Production Time
Different finishes can impact the cost and production time of the molded parts. More complex finishes, such as textured or high-gloss, may require additional mold modifications or post-processing steps, influencing the overall cost and lead time.
Durability and Maintenance
Some finishes may be more prone to wear, scratching, or discoloration over Time. The part’s usage environment and required durability will influence the choice of finish to ensure it meets performance expectations.
Mold and Material Compatibility
The choice of finish must be compatible with the mold material and plastic used in the injection molding process. Particular finishes may require mold treatments or plastic formulations to achieve the desired appearance and functionality.
Conclusion
Injection molding surface finishes play a pivotal role in determining molded parts’ final appearance and functionality. Each finish offers unique characteristics suited to different applications and design requirements, from glossy and matte to textured and metallic. By understanding the various types of finishes and the factors influencing their selection, manufacturers can achieve the desired aesthetic and functional qualities for their injection-molded products.
Whether aiming for a high-gloss, mirror-like appearance or a rugged, textured surface, carefully considering mold design, material properties, and processing conditions is essential to achieving a successful and consistent surface finish. As technology and techniques advance, the range of achievable surface finishes in injection molding will expand, offering even more possibilities for innovation and design excellence.
For more about injection molding surface finish and the different types, you can pay a visit to Djmolding at https://www.djmolding.com/about/ for more info.



